The plasma clotting cascade consists of a series of reactions involving the activation of zymogens (inert precursors of enzymes) via limited proteolysis The resulting enzymes are catalytically active serine proteases, yet they have low inherent enzymatic activity as isolated proteins Binding of a typical clotting protease to a specificHow you will use this image and then you will be able to add this image to your shopping basketClotting Science 1964; the idea of a sequence of proteases, acting as a biological amplifier \(apoptosis and complement also work this way but the coagulation cascade was described first this was a groundbreaking idea\)

How I Teach The Coagulation Cascade
Clotting cascade image
Clotting cascade image- It seems as though the clotting cascade is something you can study over and over again and it never sticks The important things to know are HEPARIN affects factor VIII in the INTRINSIC pathway and this is measured using PTT (partial thromboplastin time) WARFARIN affects the vitamin K dependent synthesis of some clotting factors (purple in the image), particularlyBrowse 71 coagulation cascade stock photos and images available or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images thrombus, illustration coagulation cascade stock illustrations illustration of a blocked artery coagulation cascade stock illustrations red blood cells flowing through the blood stream coagulation cascade stock



Coagulation Cascade Illustration
Created by Patrick van NieuwenhuizenWatch the next lesson https//wwwkhanacademyorg/science/healthandmedicine/humananatomyandphysiology/introductionBrowse 1,697 coagulation stock photos and images available, or search for coagulation cascade or coagulation test to find more great stock photos and pictures Doctor observes a blood clot expelled by a COVID19 patient at Hospital General de Mexico onCoagulation Cascade The bloodclotting protein Factor X is composed of a heavy protein chain and a light protein chain The heavy chain contains the active site where prothrombin is cleaved during the last steps of the coagulation cascade The light chain (not shown) anchors Factor X to the phospholipid membrane of platelets during
The effect of LMW heparins on thrombin is less than that of unfractionated heparin Fondaparinux is a synthetic pentasaccharide based on the minimal antithrombinExplore Staci DavisGerle's board "Clotting cascade" on See more ideas about hematology, medical laboratory science, coagulation cascadeThis document was created by Alex Yartsev (dralexyartsev@gmailcom);
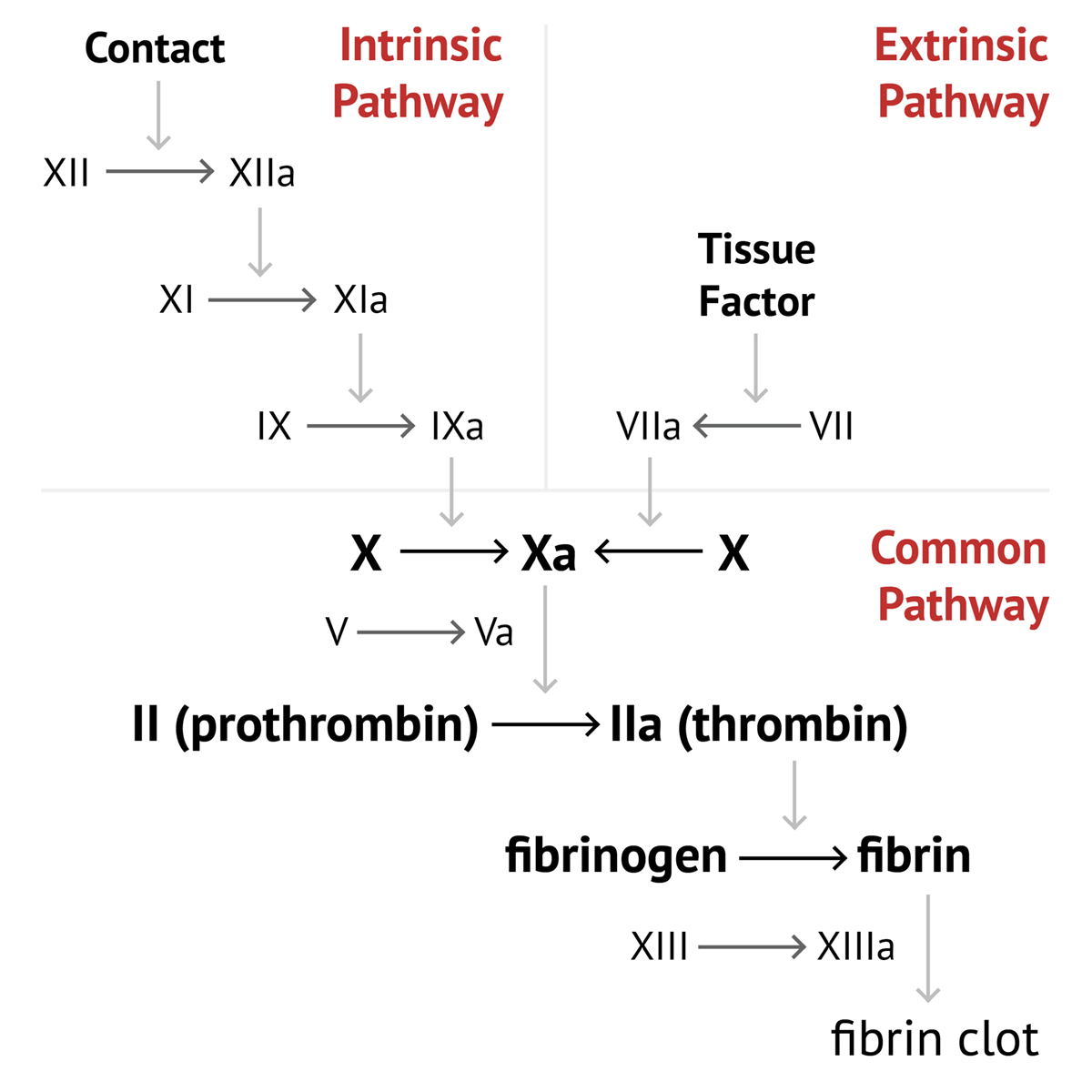
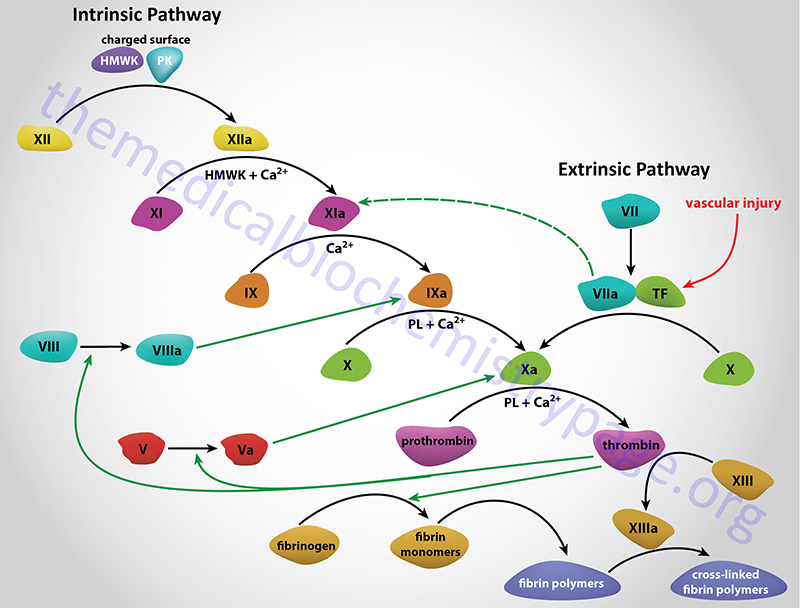
Coagulation cascade Anticoagulant effects LMW heparins include enoxaparin, dalteparin, and tinzaparin Unfractionated heparin and LMW heparin inhibit both factor Xa and thrombin; The Coagulation Cascade Blood Clotting in More Detail Blood clotting occurs in a multistep process known as the coagulation cascade The process involves many different proteins The cascade is a chain reaction in which one step leads to the next In general, each step produces a new protein which acts as an enzyme, or catalyst, for the nextA diagram is provided below of the testing coagulation cascade that shows the factors that make up the intrinsic, extrinsic, and common pathways Fibrin is the most important part of the clotting cascade because fibrin is what traps the platelets, and is therefore clotting factor number 1 Thrombin is the second most important part




Schematic Diagram Of The Coagulation Cascade And Possible Interference Download Scientific Diagram



Coagulation Cascade Illustration
Image with detailed information about each coagulation factor The coagulation cascade occurs on phospholipid cell surface membranes platelets, collagen in which clotting factors bind to the membrane to begin secondary hemostasis Formation of extrinsic and intrinsic factor tenasesBlood Clot Cell Artery Blood Clot, Vein, Artery, Tunnel, Red Blood Cells, Internal Body, Blood Cell, Heart 3d illustration of a constricted and narrowed artery and the blood cannot flow properly called arteriosclerosis coagulation stock pictures, royaltyfree photos & images Coagulation is the formation of a blood clot (or thrombus), and is essential to haemostasis Haemostasis is the body's physiological response to stop or prevent bleedingThe coagulation process is characterised by a cascade where one event sets off another and so on In the clotting/coagulation cascade, proteins called clotting factors initiate reactions which




Coagulation Cascade Image Library Thrombosis Adviser
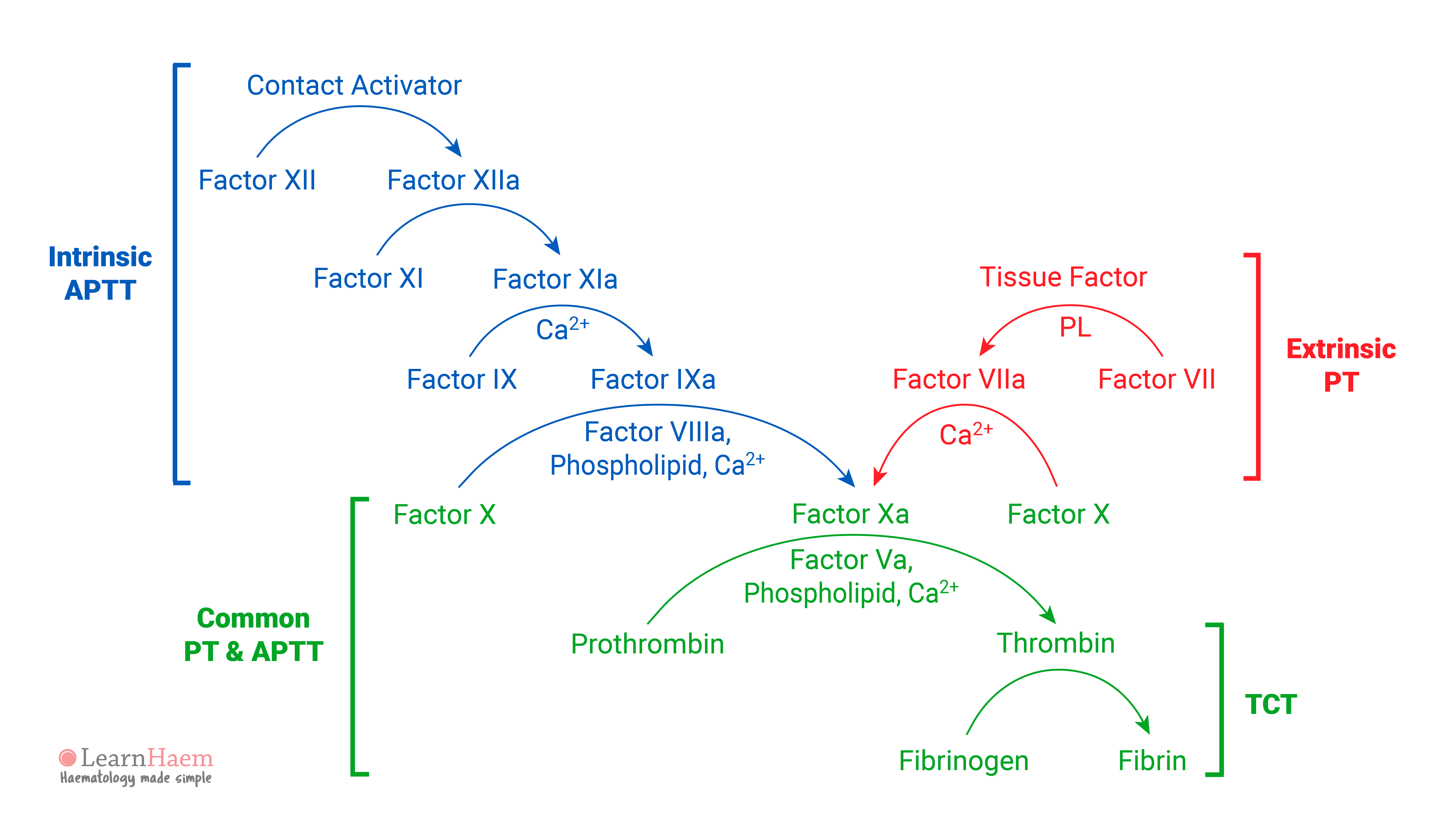



The Revised Coagulation Cascade Learnhaem Haematology Made Simple
Factor VIII (antihemophilic factor) is the protein that is deficient or defective in patients with classical hemophilia and Von Willebrand syndrome Factor VIII in plasma is thought to be associated in a complex with the highest molecular weight multimers of another glycoprotein, Von Willebrand prot The picture of clotting cascade suggest it is VIII but the text says VII Thank you "Note that – once activated, thrombin can act as a 'catalyst' in other areas of the cascade to speed up the process It can activate factor VII directly " A coagulation cascade is the process by which the body forms blood clots to prevent excess blood loss Coagulation begins with the extrinsic pathway, which activates clotting as a result of tissue injury, or the intrinsic pathway, which forms clots in response to abnormalities in the wall of a blood vessel in the absence of tissue injury



1




Clotting Cascade Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clotIt potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repairThe mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrinCoagulation Cascade • extrinsic pathway begins when trauma to vasculature exposes tissue factor to blood • activating coagulation factor VII (FVII) • active FVII complex initiates and amplifies the coagulation cascade Coagulation Cascade • intrinsic pathway activates factor XII upon surface damage resulting in downstreamOld model Normal coagulation cascade Turecek PL et al Vox Sang 1999;
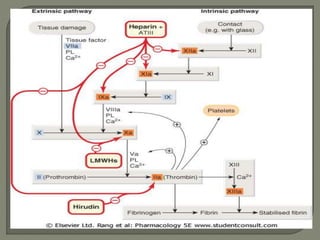



Coagulation Cascade




The Clotting Cascade Stock Photo Picture And Royalty Free Image Image
The Revised Coagulation Cascade This depicts the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of the revised model of the coagulation cascade Although this is not how coagulation works in vivo (it cannot be, as it does not explain why haemophilia is a bleeding disorder, or why factor XII deficiency is not associated with a bleeding tendency), it is stillSeveral coagulation cascade models have The Clotting Cascade Diagram Help by adding tags An image of both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of the clotting cascade including the interactions between the two and other finer details Authored By Leah Flanagan on Sunday 17th April 16
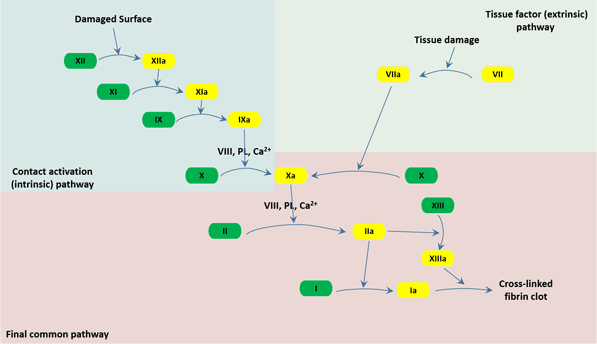



The Overview Of Coagulation Cusabio




The Coagulation Cascade Youtube
Clotting Cascade image What is the main goal of Phase 1 of clotting To help platelets stick together & prepares IIB/ IIIA receptor sites to receive collagen What factor in phase 1 of clotting is inhibited by the following antiplatelet drugs;If I have used your data or images and forgot to reference you, please email me From "William Hematology" by Lichtman et al, especially chapter 115 by Monroe III Halflives of the Coagulation Cascade Factors Factor II (Prothrombin) o Factor XII Half life 60 hrsBlood coagulation cascade, artwork C016/9873 Rights Managed 604 MB (600 MB compressed) 4770 x 4429 pixels 404 x 376 cm ⏐ 159 x 148 in (300dpi) This image is not available for purchase in your country Please contact your Account Manager if you have any query Request PRICE Add To Basket




Coagulation Cascade Video Organ Systems Khan Academy




How Does Calcium Assist In Blood Clotting Quora
An image of both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of the clotting cascade including the interactions between the two and other finer detailsThere are a few key points to focus on Disseminated intravascular coagulation is an emergency so we need to act fast!Link this page If you would like a large, unwatermarked image for your web page or blog, please purchase the appropriate license Close
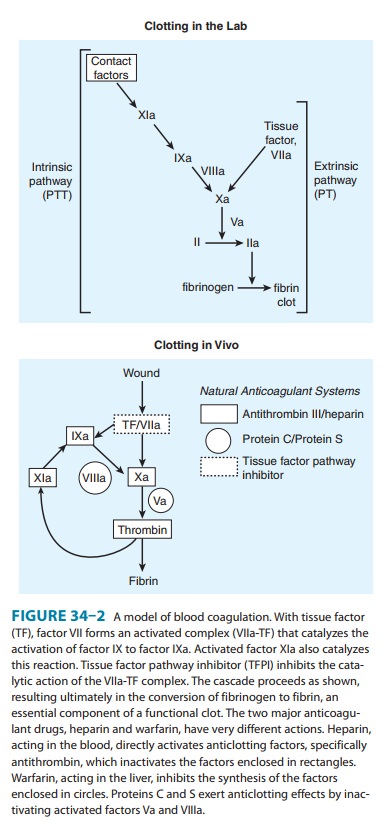



Blood Coagulation Cascade




Anaesthesia Uk Coagulation Classical Model
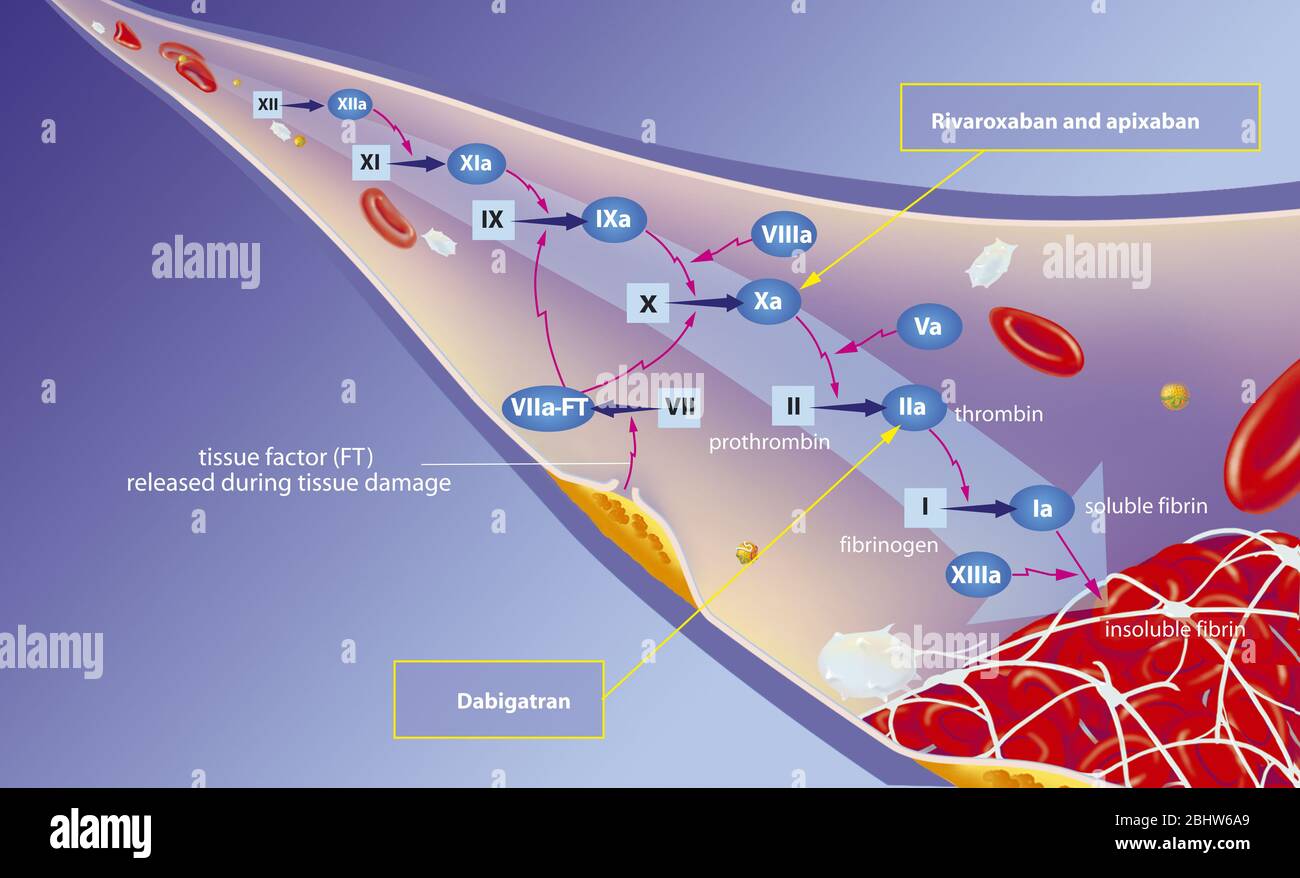
Download high quality TIFF image Clotting Cascade Tissue factor starts a cascade of interactions that lead to formation of a clot The first step occurs when factor VII, which is found in the blood, binds to tissue factor When it binds to tissue factor,77 (suppl 1) 7279 PL = Phospholipids FV FVIIa FVII TF Extrinsic Pathway Blood coagulation Common Pathway Leading to Clot FII FIIa (Thrombin) FVa Fibrinogen Fibrin CLOT Fibrin Polymer FXIIIa FXIII Intrinsic FX Pathway FXII FXIIa FXI FXIa FIX FIXa CaPL FVIII FVIIIaBrillenta (Ticagrelor) Plavix (Clopidogrel)




66 Clotting Cascade Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
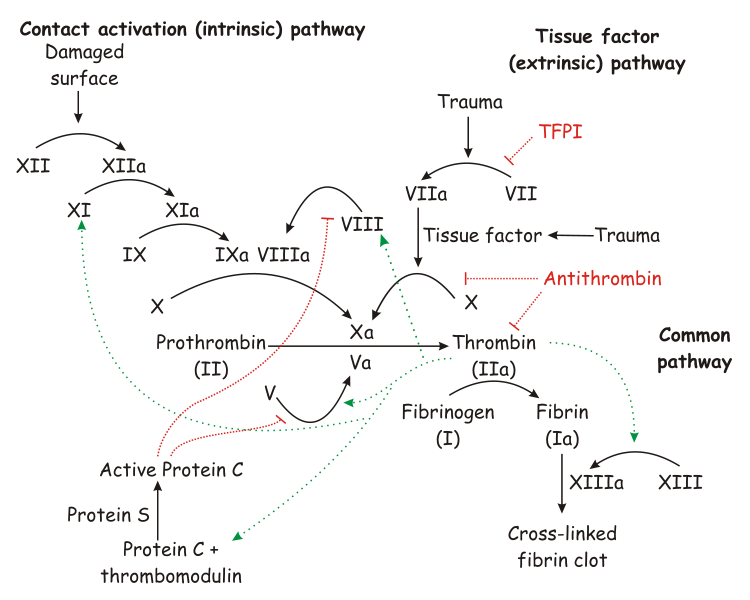



Coagulation Wikidoc
Cascade of Clotting Factors and Sites of Action of Heparin and Warfarin Variant Image ID Add to Lightbox Save to Lightbox Email this page;Find Clotting Cascade Labeled Diagram Vector Illustration stock images in HD and millions of other royaltyfree stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the collection Thousands of new, highquality pictures added every dayDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation or DIC happens when the clotting cascade is stimulated and overreacts sending microclots throughout the system This process consumes the patient's clotting factors so they can't clot anymore and we begin to see massive hemorrhage They bleed from everywhere




Schematic Representation Of The Coagulation Cascade And The Download Scientific Diagram




Clotting Cascade Nursing Mnemonics Medical Mnemonics Mcat Study
Explore abeer noor's board "Coagulation", followed by 1,856 people on See more ideas about hematology, coagulation cascade, medical laboratory The coagulation cascade is an amplification mechanism which activates clotting factors in order to produce fibrin Participating factors in the coagulation cascade can be either enzymes or cofactors Clotting Cascade 22/4/07 (Image) By Joe D (Own work) Coagulation Cascade Factors 9 images pharmacology of heparin and related drugs, clotting factors coagulation cascade youtube,



1
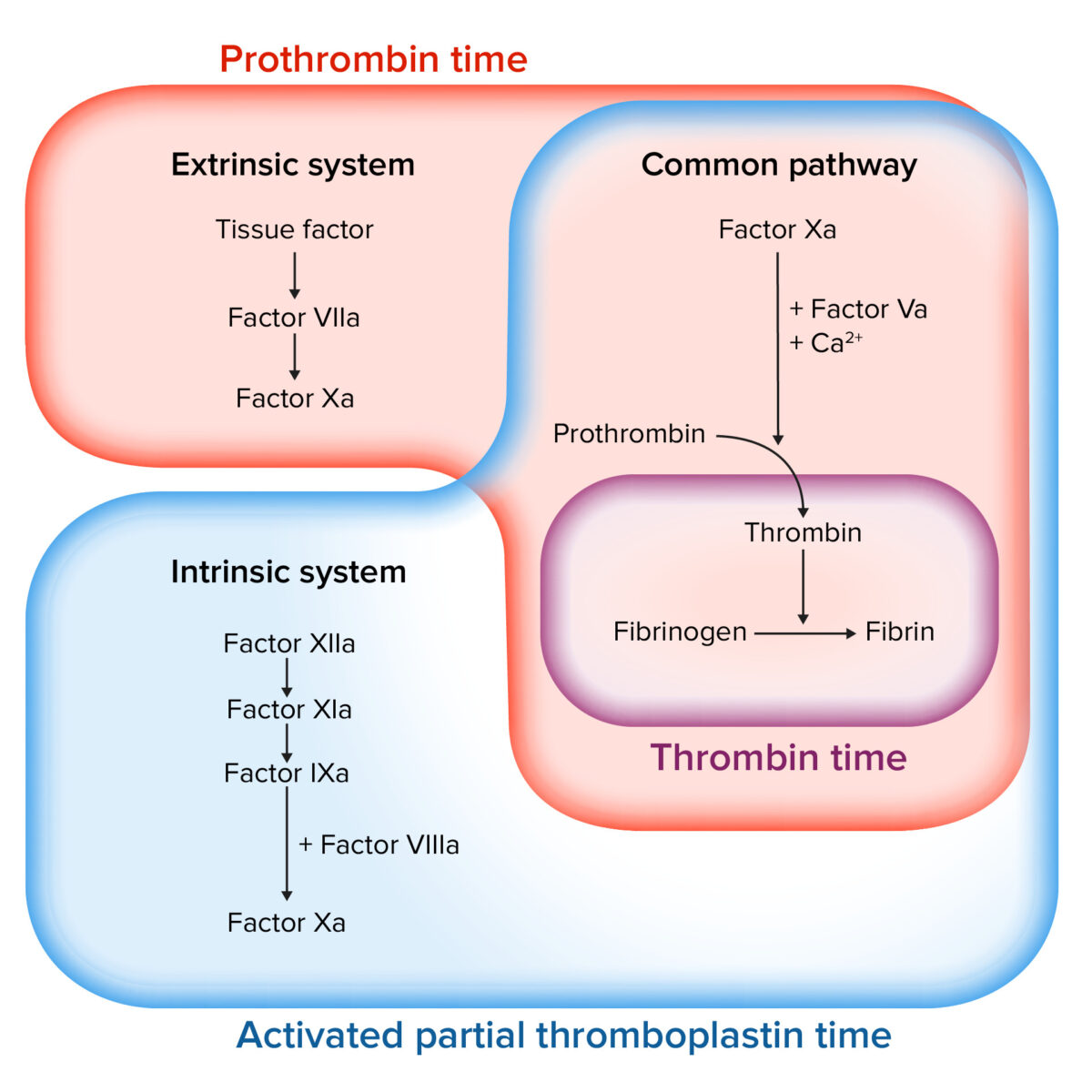



Anticoagulants Concise Medical Knowledge
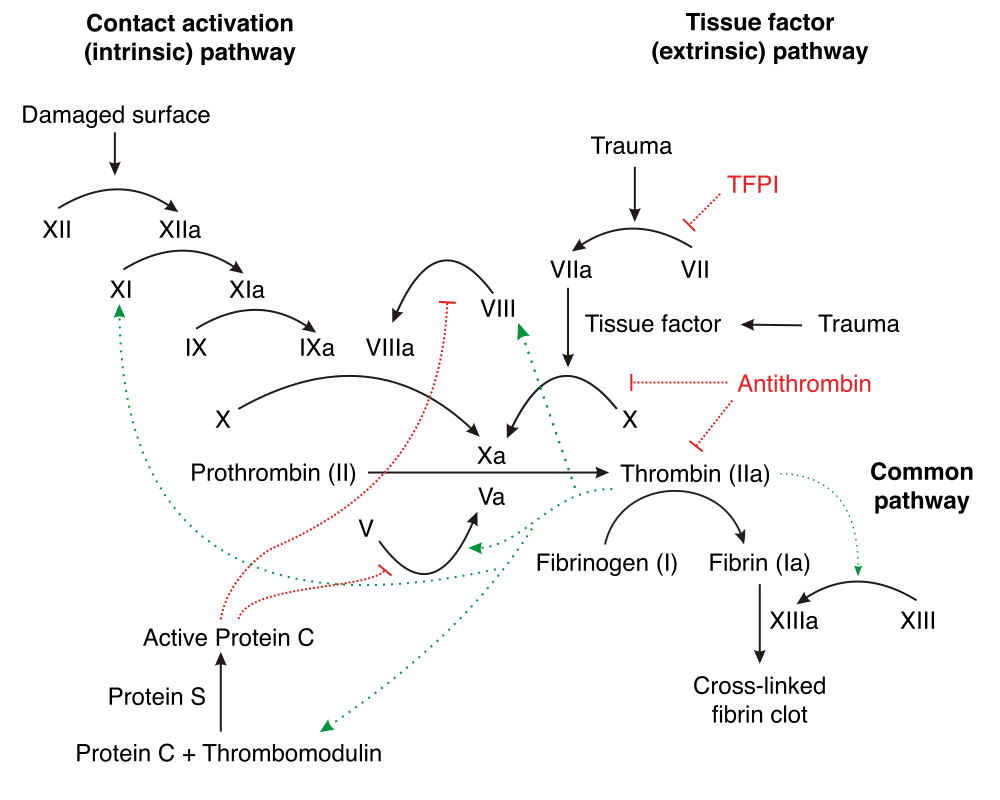
The coagulation cascade represents the strategies the body has for forming blood clots Basically, there are 2 different options for starting the cascade Image Think of the body as a highway system The bloodstream is the interstate, and the organs are the rest stopsThe coagulation factors circulate as inactive zymogens The coagulation cascade is classically divided into three pathways The tissue factor and contact activation pathways both activate the final common pathway of factor X, thrombin and fibrin Figure 1 Blood coagulation cascade (Image from Wikimedia / licensed under Creative Commons) The common pathway The common pathway begins with activation of factor X (to factor Xa) via either the extrinsic pathway or the intrinsic pathwayIt is the final stage of the coagulation cascade and leads to the formation of thrombin and fibrin Factor Xa combines with factor V, platelet membrane phospholipids and Ca 2 ions to convert prothrombin into thrombin




Coagulation Cascade Simplest Explanation The Extrinsic And Intrinsic Pathway Of Hemostasis Youtube




Coagulation Wikipedia
Image Library Coagulation Cascade Anticoagulants coagulation cascade Vitamin K antagonists lower levels of factors II, VII, IX and X The heparins and fondaparinux work Download Cascade overview An overview of the coagulation cascade, showing the initiation, propagation, and clot formation phases DownloadThere is an overreaction of the clotting cascade so the body will continuous bleed and clot Remember this will cause tiny clots and thrombosis inCascade of Clotting Factors and Sites of Action of Heparin and Warfarin Variant Image ID 1033 Add to Lightbox Save to Lightbox Email this page Link this page Print Please describe!
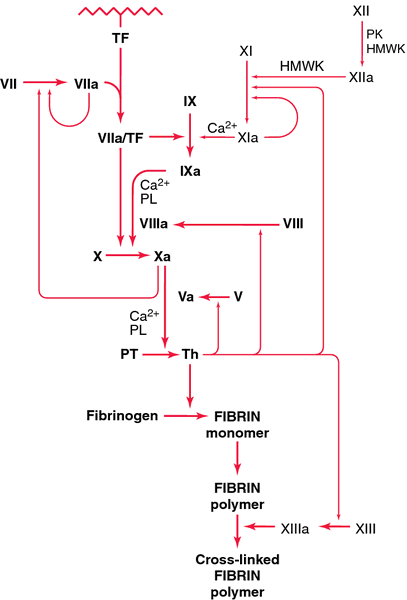



Coagulation Cascade Definition Of Coagulation Cascade By Medical Dictionary




How I Teach The Coagulation Cascade
Overview of the Coagulation Cascade Fibrinogen XIIa XI VIII Pro Thr IX X Platelet or EC PL VII Ca VIIa TF Ca PL Fibrin Crosslinked Fibrin Thr Thr XIII XIIIa TF PK XIa Coagulation Pathway IXa VIIIa Ca PL Xa Va V Ca PL XII HMWK Ca EC Endothelial cell HMWK High molecular weight kininogen NCS Negatively charged surface PL PhospholipidThrough activation of the clotting cascade (see image) and secondary hemostasis, this initial platelet plug will get reinforced to a sturdy fibrin clot The clotting cascade operates through a dual process system in which the various clotting factors become activated with the result being the formation of a fibrin strand or clot at the site ofThe coagulation process The coagulation process that leads to haemostasis involves a complex set of reactions involving approximately 30 different proteins1 These reactions convert fibrinogen, a soluble protein, to insoluble strands of fibrin, which, together with platelets, forms a stable thrombus;



Coagulation Cascade Stepwards




The Clotting Cascade Made Easy Nurse Your Own Way




Blood Clotting Cascade Diagram Quizlet




Coagulation Cascade What Is It Steps And More Osmosis



Natalies Casebook




Clotting Cascade Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Coagulation Cascade Medical Laboratory Science Medical Laboratory Technician Medical Knowledge




Coagulation Cascade Image Library Thrombosis Adviser




File Blood Clotting Cascade Chem114a Jpg Wikimedia Commons




The Clotting Cascade Made Easy Nurse Your Own Way




Understanding The Clotting Cascade Regulators And Clinical Modulators Of Coagulation Intechopen
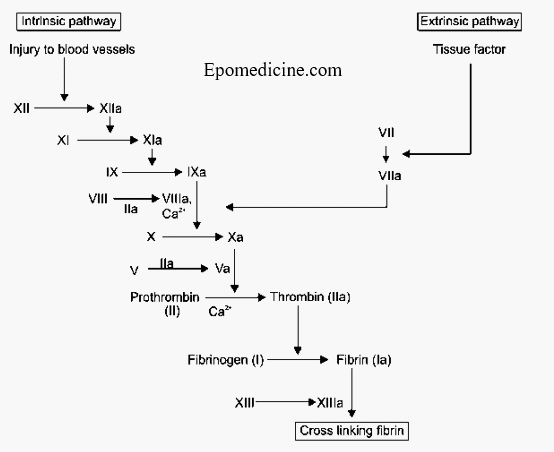



Simple Coagulation Cascade With Mnemonics Epomedicine




A Simplified Representation Of The Coagulation Cascade Ppt Download




Rethinking The Coagulation Cascade Semantic Scholar




Coagulation Cascade And Anticoagulant Sites Of Action Grepmed




The Coagulation Cascade See Online Version For Colours Download Scientific Diagram
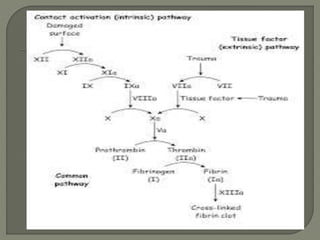



Coagulation Cascade




Prothrombin Biochemistry Britannica




Overview Of Coagulation Cascade Diagram Of The Multistep Intrinsic Download Scientific Diagram



1
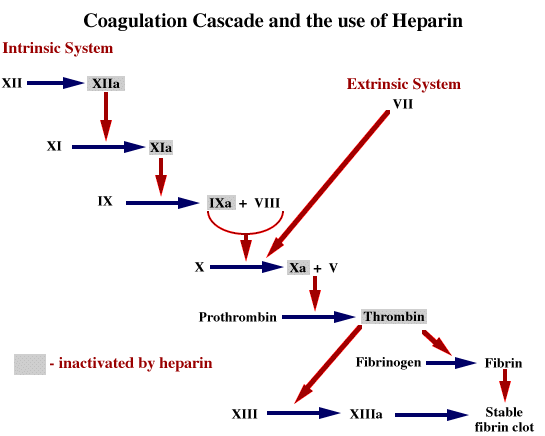



Introduction



Clotting Cascade




Figure 1 1 The Coagulation Cascade Non Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants Ncbi Bookshelf




Clotting Cascade Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
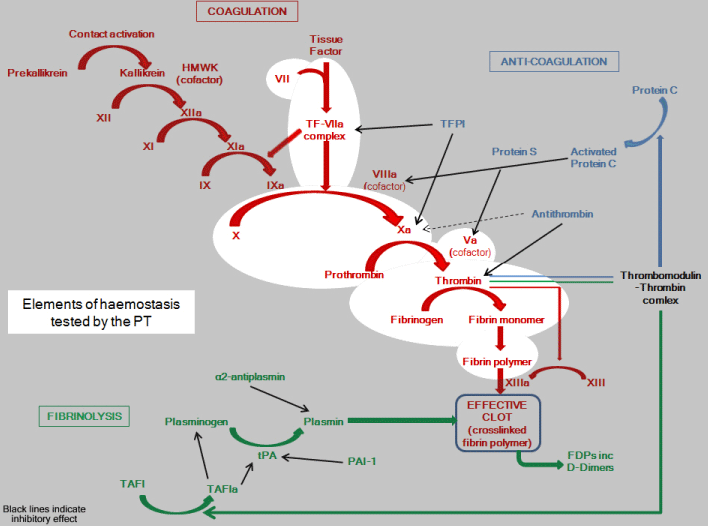



Clotting Cascade Medlibes Online Medical Library




Overview Of The Coagulation Cascade Current Approaches To Anticoagulation Non Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants



1



Coagulation Diapharma




My Notes For Usmle Mynotes4usmle Clotting Cascade I Ve Seen This




15 Coagulation Cascade Ideas Medical Laboratory Science Coagulation Cascade Medical Laboratory



Natalies Casebook




Blood Coagulation Cascade Products And Pathway C
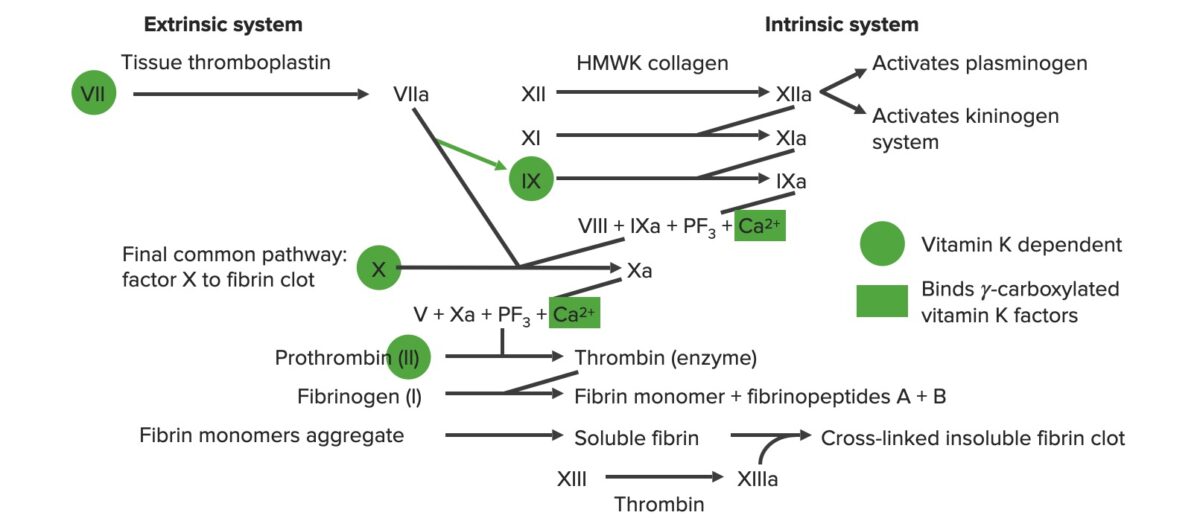



Anticoagulants Concise Medical Knowledge



Coagulation Intrinsic Extrinsic Fibrinolysis Teachmephysiology




Coagulation Cascade Flashcards Quizlet




Coagulation Wikipedia



Coagulation And The Clotting Cascade Almostadoctor




Clotting Pathway




Agents Affecting Blood Clotting Anticoagulant Agents Prevent The Extension And Formation Of Clots Inhibition By Interference With The Coagulation Cascade Ppt Download



Interpreting Coagulation Studies Coagulation Medschool




The Coagulation Cascade 72 Legend This Is The Physiological Download Scientific Diagram




Coagulation Wikipedia




Coagulation Cascade Hematology Medbullets Step 1




File Blood Clotting Cascade Png Wikipedia




How It All Starts Initiation Of The Clotting Cascade Abstract Europe Pmc




Understanding The Clotting Cascade Regulators And Clinical Modulators Of Coagulation Intechopen




Blood Clotting And The Coagulation Cascade Dopamine Endocrine And Oncogenic Functions




The Clotting Cascade Diagram On Meducation Medical Laboratory Science Medical Technology Medical Laboratory




Quantitative Assessment Of The Blood Coagulation Cascade




Blood Coagulation Cascade Artwork Stock Image C016 9873 Science Photo Library



Hemostasis Biochemistry Of Blood Coagulation The Medical Biochemistry Page



Coagulation Cascade Memes Memes Www Medicaltalk Net The Best Medical Forum For Medical Students And Doctors Worldwide




Clotting Cascade Google Search Medical School Studying Medical Lab Technician Medical Education




Clotting Cascade Labeled Diagram Stock Vector Royalty Free




Coagulation Cascade Medical Education Facebook




Review Of The Coagulation Cascade Traditional Model Grepmed




How I Teach The Coagulation Cascade



Coagulation Cascade High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



15 Coagulation Cascade Ideas Medical Laboratory Science Coagulation Cascade Medical Laboratory



Coagulation Cascade Stepwards
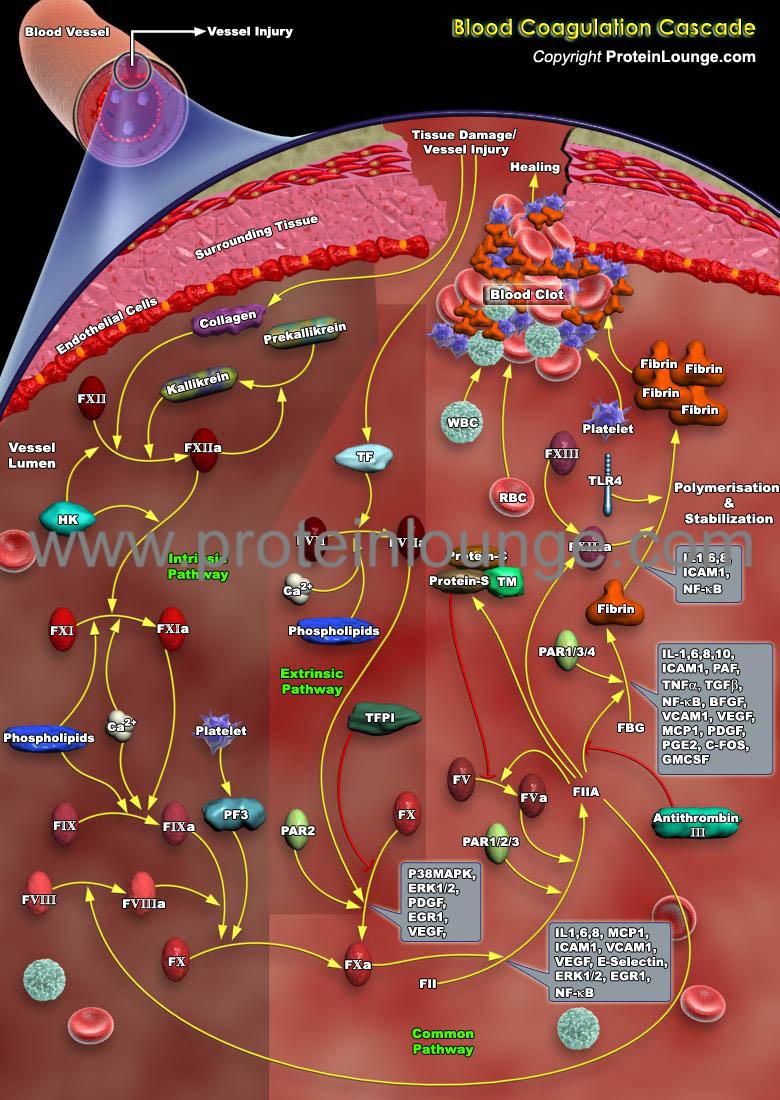



Biological Databases And Tools Blood Coagulation Cascade Protein Lounge




Review Article Coagulation Cascade And Therapeutics Update Relevance To Nephrology Part 1 Overview Of Coagulation Thrombophilias And History Of Anticoagulants Adams 09 Nephrology Wiley Online Library




The Coagulation Cascade In Cirrhosis Clinics In Liver Disease




Coagulation Cascade In Cm Data Show Differential Regulation Of Download Scientific Diagram




Coagulation System An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
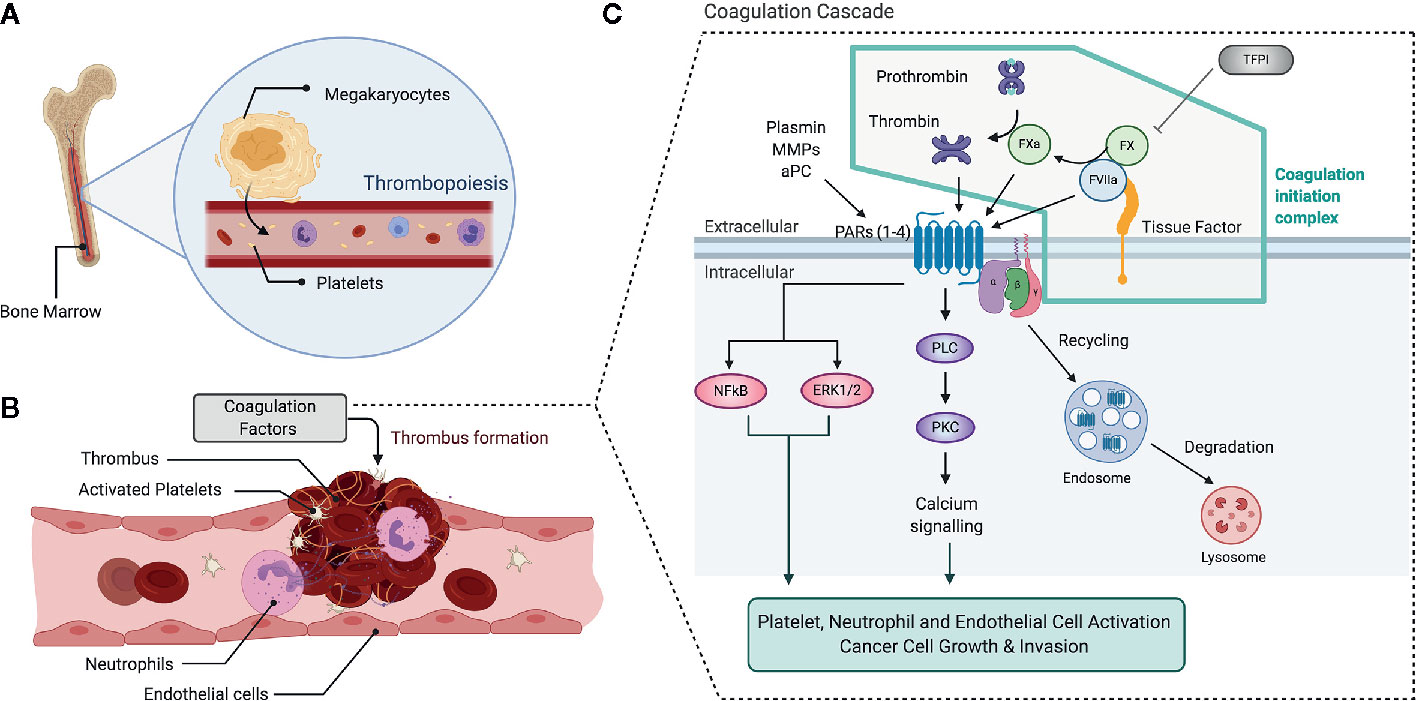



Frontiers Deciphering The Role Of The Coagulation Cascade And Autophagy In Cancer Related Thrombosis And Metastasis Oncology



Secondary Hemostasis Coagulation Cascade Calgary Guide




Coagulation Pocket Dentistry



The Coagulation Cascade




Coagulation Pathway It Takes 30




How Does The Clotting Cascade Work Quora




Anticoagulant Wikipedia




Coagulation Factors Enzyme
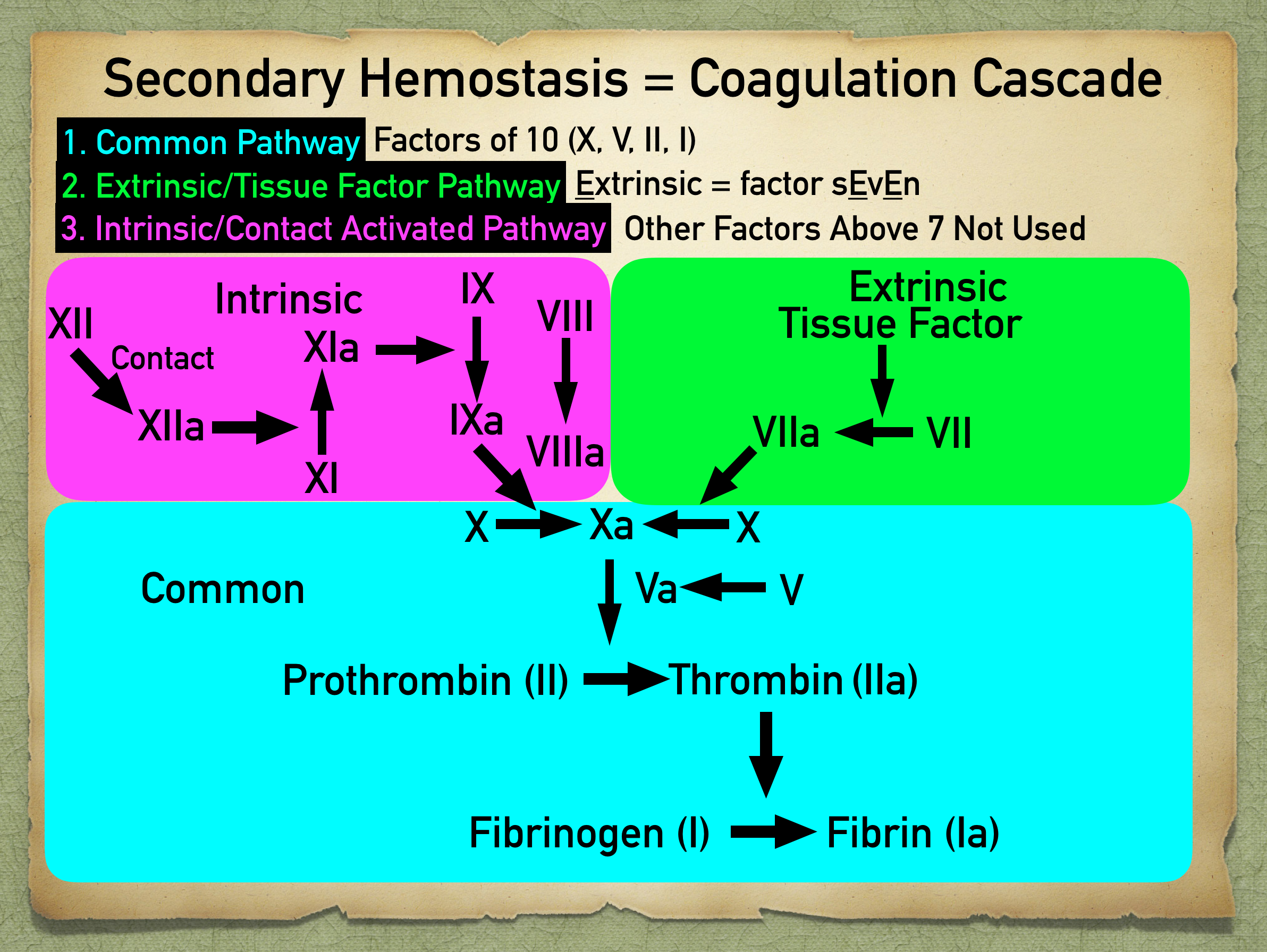



Secondary Hemostasis Definition And Coagulation Cascade Pathway Steps With Ppt Diagram Of Factors Ezmed
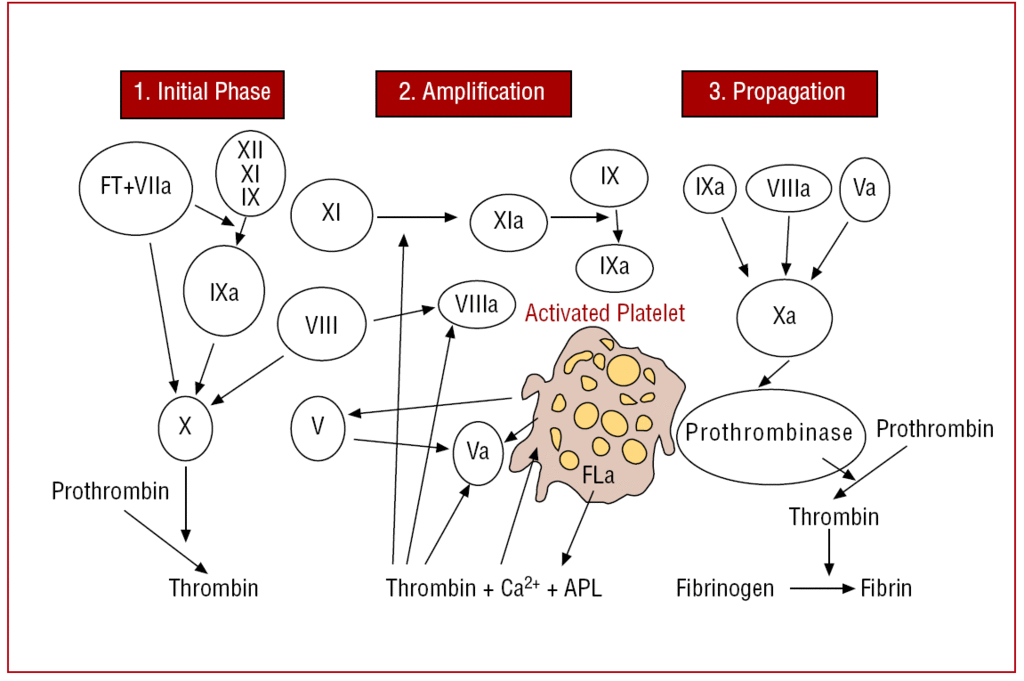



The New Coagulation Cascade And Its Possible Influence On The Delicate Balance Between Thrombosis And Hemorrhage Revista Espanola De Cardiologia




Coagulation Cascade Download Scientific Diagram




Coagulation Cascade Image Library Thrombosis Adviser
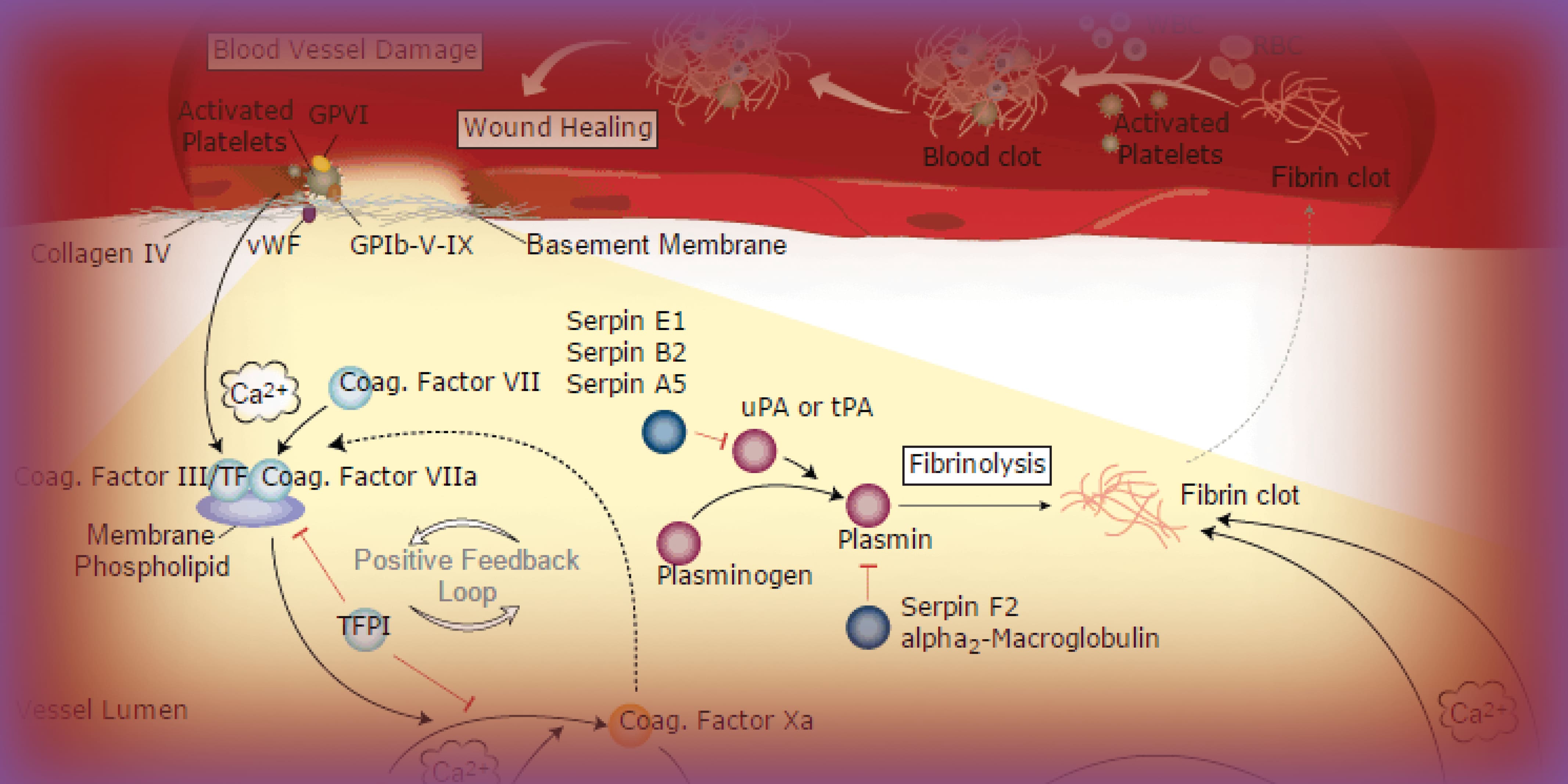



Blood Coagulation Pathway And Resources




The Choreography Of Clotting And On Another Note




Learn About Clotting Cascade Chegg Com



No comments:
Post a Comment